Ganesha

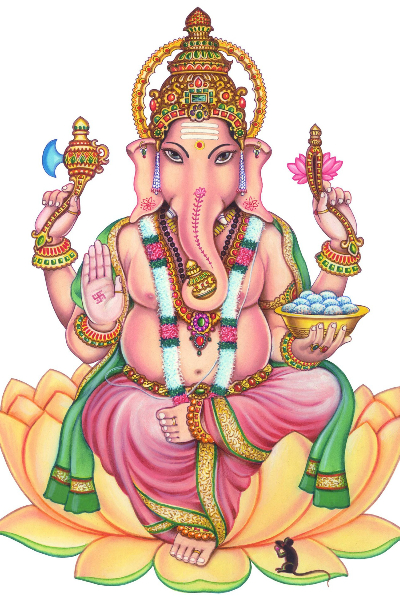
Ganesha , also known as Ganapati, Vinayaka and Binayak, is one of the best-known and most worshiped deities in the Hindu pantheon.His image is found throughout India, Sri Lanka, Thailand and Nepal. Hindu sects worship him regardless of affiliations. Devotion to Ganesha is widely diffused and extends to Jains and Buddhists.
Although he is known by many attributes, his elephant head makes him easy to identify. Ganesha is widely revered as the remover of obstacles, the patron of arts and sciences and the deva of intellect and wisdom. As the god of beginnings, he is honoured at the start of rites and ceremonies. He is also invoked as patron of letters and learning during writing sessions. Several texts relate mythological anecdotes associated with his birth and exploits and explain his distinct iconography.
He emerged as a distinct deity in the 4th and 5th centuries AD, during the Gupta period, although he inherited traits from Vedic and pre-Vedic precursors. He was formally included among the five primary deities of Smartism (a Hindu denomination) in the 9th century. A sect of devotees called the Ganapatya arose, who identified him as the supreme deity. The principal scriptures dedicated to him are the Ganesha Purana, the Mudgala Purana, and the Ganapati Atharvashirsa. Brahma Purana and Brahmanda Purana are other two Puranic genre encyclopedic texts that deal with Ganesha.